Mirrors come in different shapes and sizes, with plane and curved surfaces dictating their reflective properties. Understanding the characteristics of concave and convex mirrors is essential in grasping their diverse applications and optical behavior.
Before delving into the intricacies of concave and convex mirrors, let’s familiarize ourselves with key terms:
Spherical mirrors are categorized into concave and convex mirrors based on their reflective surface curvature.
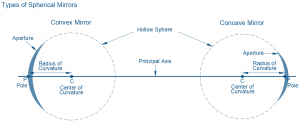
Concave mirrors feature an inwardly curved reflective surface resembling the inner section of a sphere. They converge light rays upon reflection, resulting in specific image characteristics depending on the object’s position relative to the mirror.
The behavior of concave mirrors varies with the object’s placement:
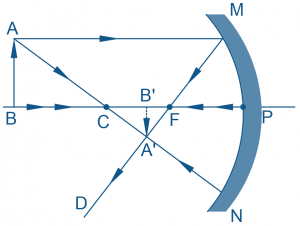
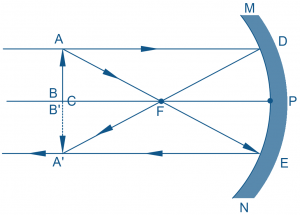
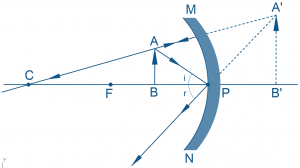
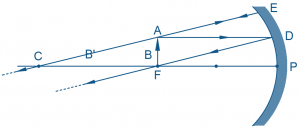
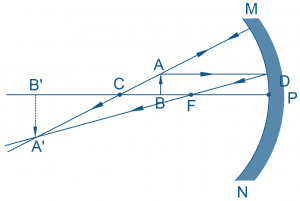
Convex mirrors possess an outwardly curved reflective surface resembling the outer section of a sphere. They diverge light rays upon reflection, leading to distinct image characteristics irrespective of the object’s position.
Convex mirrors consistently produce virtual, upright, and reduced images regardless of object placement. They lack a real focal point and offer a wide field of view, making them ideal for applications requiring broad observation angles.
Understanding how light rays behave upon incidence on concave and convex mirrors aids in predicting image formation accurately.
Concave and convex mirrors exhibit unique optical properties, crucial for various applications ranging from optical instruments to surveillance systems. Mastering their characteristics and image formation processes enhances our comprehension of light behavior and facilitates efficient utilization in diverse fields.
Do not hesitate to contact Shanghai Optics today. We’d be more than happy to discuss your projects and how best they can become a success.