The human eye cannot see infrared light since this light lies beyond the visible light spectrum. However, thanks to infrared optics, it’s possible to capture infrared light.
But what is infrared optics?
Infrared (IR) optics refers to any device that can register, display and emit infrared radiation. These devices use optical elements such as an infrared filter, mirror, and infrared lenses to capture infrared light.
An IR lens captures infrared light that is virtually impossible to see with the naked eye. While a normal camera lens captures images of objects that radiate light that is visible to the eye, an infrared lens detects electromagnetic radiation, which is the light that lies beyond the visible spectrum.
Moreover, an infrared lens depends on heat rather than light to record images. Since IR light can be felt as heat, an infrared lens can be able to express the heat value of an object that radiates heat.
Infrared lenses have a wide range of industry applications. For instance, they are used in thermal imaging cameras by medical professionals. IR technology is also used by electricians and building inspectors to detect leaks, corrosion, and other building deterioration dangers.
Want to learn more?
This article explores everything you need to know about IR lenses and how they work.
The human eye is an optical device with a sensor called the retina. Regular cameras work very much like the naked eye, as they receive and turn radiation from the visible light spectrum into an image.
Unfortunately, a normal camera, just like the retina, cannot detect infrared rays.
The good news is that we can use IR cameras to detect this light. Infrared cameras require a custom lens, infrared filters, and sensors to capture IR light.
Notably, infrared camera lenses work differently from regular camera lenses.
An infrared lens works by capturing all the IR light bouncing around and redirects this light to the camera sensor, which helps create a clear thermal image. IR lenses used in infrared cameras capture invisible heat or IR radiation in extended wavelength ranges of 700 to 900 nm or more.
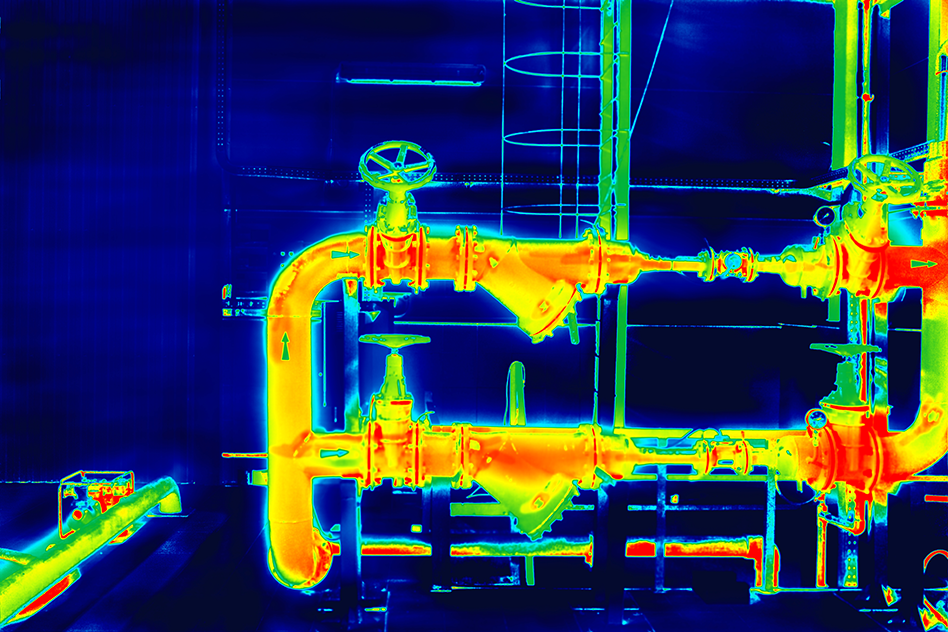
An infrared lens helps to focus the infrared radiation of the object to the camera’s sensor, which generates an amplified electrical signal that is converted to a fine image.
An IR camera lens makes images from thermal radiation, aka infrared or heat. This is why IR camera custom lenses are made of materials such as germanium, silicon, chalcogenide glass, and other substances that have low absorption and are transparent in the infrared spectrum.
The biggest advantage of infrared lenses is that they help capture images that the human eye cannot see. This means that an image taken with an infrared lens is very unique and greatly different from what is captured by a normal camera lens.
Other advantages of an IR lens include:

IR lenses are used in several applications and scenarios, as noted below.
In closing, infrared cameras use IR lenses that are sensitive to infrared heat or energy. Infrared lenses have various advantages, including the ability to capture images that are invisible to the human eye. IR lenses are also not limited by high temperatures and are also suitable for long-distance illumination. Due to their unique advantages, IR lenses can be used in several applications, including surveillance cameras, thermal imaging cameras, and infrared photography.