Aspherical optics have revolutionized optical systems, promising enhanced performance and versatility. However, their complex geometry demands meticulous metrology techniques for precise manufacturing and quality assessment. In this article, we delve into the intricate world of asphere metrology, exploring advanced methods and their implications for optical engineering.
Unlike traditional spherical lenses, aspheres boast non-spherical curvature profiles, crucial for correcting aberrations and improving optical performance. These intricate optics defy simple geometric description and are characterized by polynomial equations.
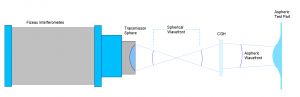
CGH transforms spherical wavefronts into aspheric ones, essential for asphere metrology.
| Metrology Method | Full Surface Map | PV | RMS | Flexible Lens Geometry | Time of Measurement | Precision | Cost |
| 2D Contact Profilometry | Yes | Yes | High | Short | High | Low | Low |
| Stitching Interferometry | Yes | Yes | Yes | Intermediate | Long | High | High |
| Computer-Generated Holography | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low | Intermediate | Medium | Low-High |
| Chromatic Confocal Sensing | Yes | Yes | Yes | Intermediate | Long | Low | Moderate |
| Multiwavelength Interferometry | Yes | Yes | Yes | Intermediate | Short | High | High |
As the demand for aspherical optics grows, mastering asphere metrology becomes imperative. At Shanghai Optics, we specialize in crafting high-quality custom aspheres and offer tailored metrology solutions to meet diverse requirements. With meticulous attention to detail, we ensure optimal performance and reliability in every optical system.
Contact Shanghai Optics today! We’d be more than happy to discuss your projects and how to best bring them to fruition.