Exploring Beam Splitters: Types and Applications
What Is a Beam Splitter? Working Principles, Types, and Applications
Beam splitters play a critical role in modern optical technology, powering devices from teleprompters and holographic displays to fiber-optic networks and advanced scientific instruments. Despite their simple appearance, these optical components are fundamental to many high-tech systems we use daily.
This guide explores what a beam splitter is, how it works, the main types of beam splitters, and their real-world applications across industries.
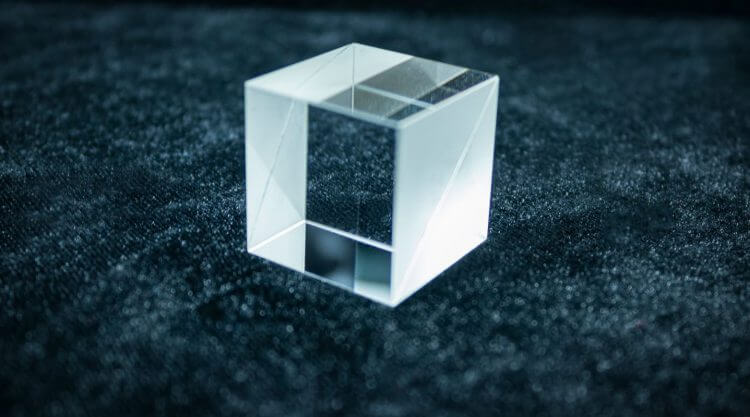


What Is a Beam Splitter?
A beam splitter is an optical device designed to divide a beam of light into two separate paths. Most beam splitters are made from glass cubes coated with thin reflective layers. When a light beam enters the cube:- Part of the light transmits through the material
- The remaining portion reflects at a precise angle
How Beam Splitters Work
Beam splitters rely on optical coatings and partial reflection principles. The exact transmission-to-reflection ratio depends on:- Coating composition (metallic or dielectric)
- Thickness of the optical layer
- Light wavelength and polarization
Beam Splitter Types
1. Cube Beam Splitter
Constructed from two right-angle prisms bonded with optical resin or epoxy.- Allows tailored splitting ratios
- Can incorporate polarizing or wavelength-selective coatings
2. Plate Beam Splitter
Also called a dielectric mirror, made from thin coated glass placed at 45°.- Equal reflection and transmission
- Available in IR materials (e.g., CaF₂, KBr) for specialty wavelengths
3. Polarizing and Non-Polarizing Beam Splitters
| Type | Function |
| Non-polarizing | Maintains original light polarization |
| Polarizing | Separates light into S-polarized and P-polarized beams |
4. Dichroic Beam Splitter
Separates light by wavelength, making it essential for:- Fluorescence microscopy
- Laser beam combining
- Imaging systems
5. Other Beam Splitter Designs
- Pellicle beam splitters
- Fiber-optic beam splitters
- Polka-dot beam splitters
- Multi-output beam splitters
Beam Splitter Coatings
Beam splitter coatings optimize reflection, transmission, and polarization control while preventing light loss. Common coatings include:- Thin metal layers
- Dielectric oxide coatings
Teleprompters
Beam splitter glass allows presenters to read scripts without shifting eye contact, crucial for:- Broadcast media
- Political speeches
- YouTube and livestream production
Holography
Splits light into reference and object beams to create 3D holographic effects — often requiring a black background for clarity.Interferometry
Essential for precision distance measurement using interference patterns. Used in:- Metrology
- Optical testing
- Scientific research (e.g., quantum optics)
Additional Uses
Beam splitters are vital across industries:- Robotics and automation
- Fiber-optic communication
- Machine vision
- Security cameras
- Smart mirrors
- Laser technology & spectroscopy
- Film and broadcast equipment
Optical Beam Splitters in Imaging & Life Sciences
Beam splitters power advanced imaging systems:| Use Case | Beam Splitter Type |
| Fluorescence microscopy | Dichroic beam splitter |
| Co-axial illumination | Plate beam splitter |
| IR sensor protection | Hot/cold mirrors |
| Color balancing | Dichroic filters |
Conclusion
Beam splitters are essential components in optics, imaging, telecom, laser systems, and scientific research. Their ability to control light intensity, polarization, and wavelength makes them fundamental to countless technologies.
Looking for Custom Beam Splitters?
Shanghai Optics manufactures precision-engineered custom beam splitters for scientific, industrial, and commercial use.
Explore our product range and request a quote today.
For questions or custom optical design support, contact our team — we’re here to help.
FAQs
What is a beam splitter used for?Beam splitters divide light for use in optical testing, imaging, microscopy, telecommunications, lasers, and teleprompters.
What is the difference between polarizing and non-polarizing beam splitters?
Polarizing beam splitters separate light by polarization, while non-polarizing splitters maintain original polarization.
What materials are beam splitters made of?
Common materials include optical glass, fused silica, IR crystals like CaF₂ and KBr, and thin-film coatings.

